Understanding the basics of network infrastructure can be a daunting task for beginners. However, with the right guidance and resources, anyone can learn to effectively utilize this technology. This guide provides an introduction to networking concepts through simple explanations and examples.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a better grasp of how networks are structured, as well as how they work together to make data transfer more efficient and reliable. Additionally, tips on troubleshooting common issues with networks will be provided to help readers understand how best to maintain their systems.
With this knowledge in hand, users will be able to confidently navigate their way through any challenge that comes their way related to network infrastructure.
1. Introduction to Network Infrastructure Basics

Network infrastructure is a term used to describe the combination of hardware and software that provides a communication link between users, devices, and networks. A basic understanding of network infrastructure is essential for any beginner looking to build or manage an efficient networking environment.
This guide will provide an overview on the common components found in most network infrastructures such as routers, switches and hubs; how they work together to form connections; as well as some best practices for implementing them into your own setup. Routers are the central piece of any network infrastructure. They act as traffic directors, taking incoming data from one source and sending it out through another port to its intended destination.
Routers can be configured depending on your needs – whether you’re connecting two computers within the same local area network (LAN) or providing access from outside sources like remote users or Wi-Fi hotspots. Switches are similar to routers but serve a different purpose: Instead of routing data packets based off addresses, switches create direct links between devices connected to their ports.
These physical connections allow for faster transmission rates compared with routers because all data goes directly through the switch instead of being individually routed by address first before going out onto its intended recipients system. Hubs also play an important role in modern networks by serving as shared connection points between individual LAN segments when multiple subnets must communicate with each other within the same larger LAN (Local Area Network).
Hubs do not filter traffic so they tend to be less secure than both switches and routers due to their lack of security features such as firewalls or encryption protocols; however this makes them ideal for limited usage scenarios where simple connectivity is needed without needing further security measures applied.
Once you have a firm grasp on these basic building blocks that make up most corporate networks today – then you can start thinking about more advanced topics such as wireless mesh systems, virtual private networks (VPN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), Quality Of Service (QoS), IP addressing schemes, etc.
All these elements come together should give you enough knowledge base necessary when setting up your own customised network topology which could suit your particular business requirements best while keeping costs at minimum levels too!
2. Types of Network Infrastructures

Network infrastructures come in different forms, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types are Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), and Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs). Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network that connects computers or other electronic devices located within a single building or small geographic area such as an office, school, or house.
This type of network enables users to share resources like files and printers over short distances. LANs usually rely on cable media such as Ethernet cables connected to switches for connection.
Wide Area Network (WAN) is designed to span large geographical locations separated by hundreds or thousands of miles. WANs allow users from multiple offices spread across the globe to connect through leased lines provided by Internet Service Providers(ISP).
They are often used for corporate applications like email services, remote access, file sharing etc., but can also be deployed in homes if there is need for increased speeds than what regular broadband connections offer. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is similar to LAN but covers larger areas than LAN while still being smaller than WAN networks; typically covering cities and towns within a 50 km radius range.
It provides high-speed data transmission over long distances using technologies such as fibre optic cables instead of traditional copper wires used in wired networks. MAN’s are generally owned either by private companies or local government authorities who provide internet access services at affordable rates within their coverage area using this infrastructure
3. Components of a Network Infrastructure
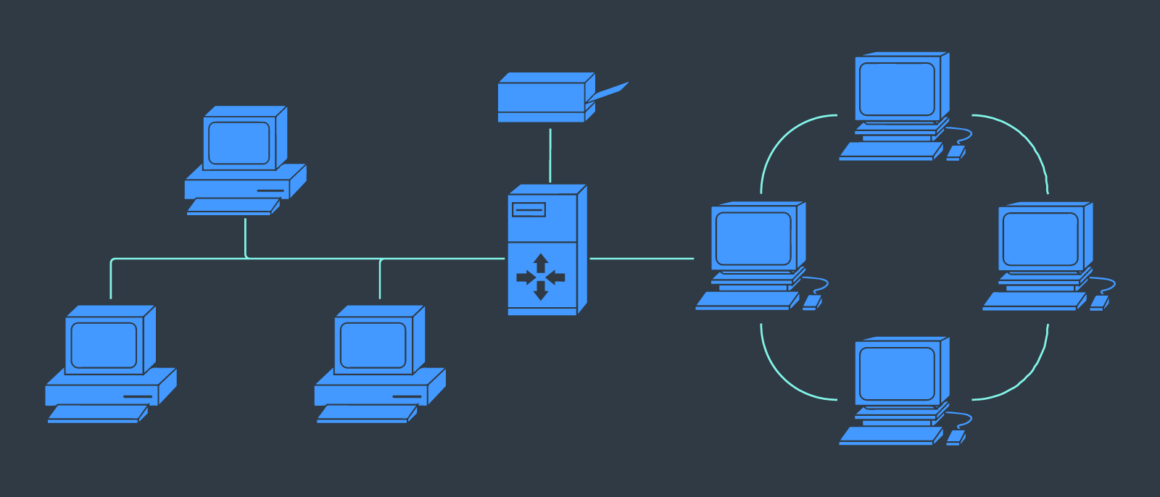
Network infrastructure is composed of a set of components that allow for the exchange and flow of data, services, and information. To understand the basics of network infrastructure, it is important to know what these components are.
First, there is hardware such as servers, routers, switches, hubs, and bridges that make up the physical layer where traffic flows through. Next comes software including operating systems such as Windows or Linux which provide an interface for users to access their applications.
Finally, there are protocols like TCP/IP that allow communication between computers on different networks without any disruption in service delivery. All these components play an integral role in ensuring reliable networking performance – understanding them will give you greater insight into how your network works!
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding the basics of network infrastructure is essential for any beginner. It can seem overwhelming at first, but with the right tools and resources, it can be relatively straightforward.
Network infrastructure provides a foundation to build on top of that helps businesses run smoothly and efficiently. Having an understanding of how networks are designed and managed will help you become more familiar with networking technology as well as identify potential problems before they become too large to handle.
As we have seen in this guide, there are several components to consider when building or maintaining your own network infrastructure. With these tips in mind, you should now have a better idea of how to get started with creating your very own successful network infrastructure setup!